The August year-over-year export and import container counts were weaker than last month with imports in contraction year-over-year.

Analyst Opinion of Container Movements
Simply looking at this month versus last month – the export rate of growth declined whilst exports also declined. The three-month rolling averages remain in positive territory – but both exports and imports trends slowing. It may be that we are seeing the impact of the trade wars.
This dataset is based on the Ports of LA and Long Beach which account for much (approximately 40%) of the container movement into and out of the United States – and these two ports report their data significantly earlier than other USA ports. Most of the manufactured goods move between countries in sea containers (except larger rolling items such as automobiles). This pulse point is an early indicator of the health of the economy.
Consider that imports final sales are added to GDP usually several months after import – while the import cost itself is subtracted from GDP in the month of import. Export final sales occur around the date of export. Container counts do not include bulk commodities such as oil or autos which are not shipped in containers. For this month:
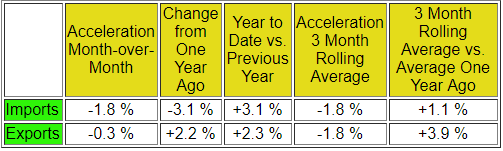
As the data is very noisy – the best way to look at this data normally is the 3-month rolling averages. There is a direct linkage between imports and USA economic activity – and the change in growth in imports foretells a real change in economic growth. Export growth is an indicator of competitiveness and global economic growth.
There is a reasonable correlation between the container counts and the US Census trade data also being analyzed by Econintersect. But trade data lags several months after the more timely container counts.
Econintersect considers import and exports significant elements in determining economic health (please see caveats below). recession levels.
















Leave A Comment