As those who frequent these pages are no doubt aware, NPLs at Chinese banks are rising.
Here’s a kind of 30,000 -foot view from RBS’ Alberto Gallo:

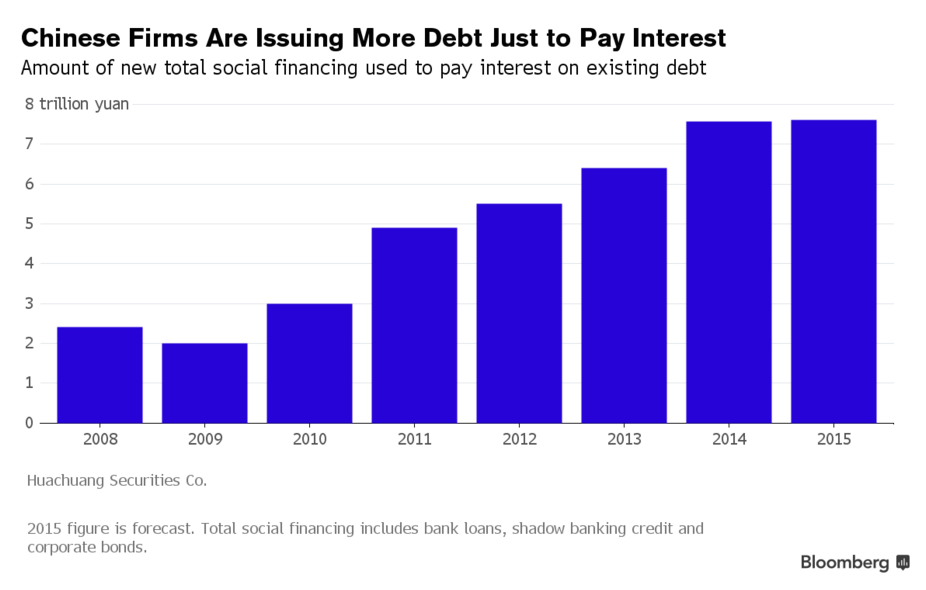
As we documented last month after data on new RMB loans showed that the credit impulse in China simply rolled over and died in October, part of the problem is that banks are becoming increasingly concerned about sour loans, as an acute overcapacity problem, a decelerating economy, and sluggish global growth and trade have conspired to create an environment in which borrowers are now taking on more debt just to service the loans they took out in the past.
As Credit Suisse noted earlier this month, some firms are now borrowing just to pay salaries. Indeed, more than 50% of debt in the commodities space was EBIT-uncovered in 2014. The takeaway: China’s Minksy Moment is nigh.
Still, the official numbers on NPLs (shown above) look surprisingly low for an economy which is supposedly careening towards a debt crisis. There’s a simple explanation for this apparent discrepancy: the numbers, like China’s official GDP prints, are fabricated.
There are a number of strategies China uses to depress the official NPL figures including compelling banks to roll bad debt, but as Fitch outlined in detail back in May, Asset Management Companies play an important role.
“China’s four major AMCs were set up in 1999 to absorb CNY1.4trn in bad assets at par value from China Development Bank and the big four banks (Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, China Construction Bank, Bank of China and Agricultural Bank of China) before their restructuring. NPL disposals to AMCs have increased in recent years as more banks have come under pressure to manage their reported NPL levels,” Fitch wrote, adding that“AMCs’ strategic importance [should] increase with China’s economic rebalancing,”
Here’s more:
Bank loan disposals to AMCs also mask underlying NPL increases, and direct asset purchases by AMCs from borrowers mean bad assets may never be formally recognised as NPLs within the banking system.
AMCs have only been granted licences from the CBRC to acquire restructured DAs directly from non-financial enterprises (NFE) since 2011. DAs purchased from these enterprises have since constantly increased as a share of the total. Fitch’s International Public Finance team estimates that 60%-70% of DAs restructured in 2010-2014 relate to the real estate sector. Many of the distressed property assets could be directly offloaded to AMCs without ever being recognised as bad loans through the banking system. This partly explains how reported NPL ratios for property loans are kept so low in China.
The primary source of traditional DAs is banks. Upon completion of debt acquisition, the AMC assumes the pre-existing rights and obligations between the banks and debtors, and realises or enhances the value of the assets primarily through debt restructuring, litigation and sales. However, most of the DAs acquired by AMCs since 2011 have come from NFEs. AMCs also buy restructured DAs from banks and non-bank financial institutions.
When AMCs acquire restructured DAs, they enter into an agreement with the creditor and debtor to confirm the contractual rights and obligations, and then acquire the debt from the creditor. The AMC, the debtor and its related parties also enter into a restructuring agreement that details the repayment amounts, the repayment method, repayment schedule, and any collateral and guarantee agreements. The restructuring returns and payment schedule are fixed at the time the restructuring agreements are made.











Leave A Comment