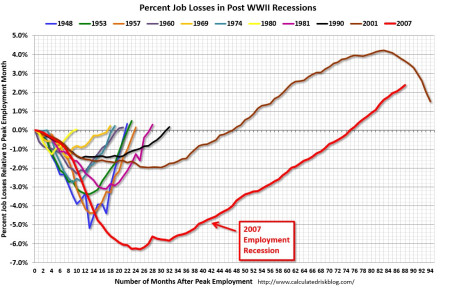
The economic recovery since the Great Financial Crisis of 2008-09 has been widely interpreted as the slowest recovery since World War II. Bill McBride of Calculated Risk captures this phenomenon incredibly well in his historical job loss chart (see red line in chart below):

Source: Calculated Risk
History tells us that the economy traditionally suffers from an economic recession twice per decade, but we are closing in on seven years since the last recession with little evidence of impending economic doom.
So, are we due? Logic would dictate that since this recovery has been the slowest in a generation, the duration of this recovery should also be the longest. Strategist Ed Yardeni of Dr. Ed’s Blog uses data from historical economic cycles and CEI statistics (Coincident Economic Indicators) to make the same case. Based on his analysis, Yardeni does not see the next recession arriving until March 2019 (see chart below). If you take a look at the last five previous cycle peaks, recoveries generally last for an additional five and a half years (roughly 65 months). Since the last rebound to a cyclical peak occurred in October 2013, 65 months from then would imply the next downturn in March 2019.

Source: Dr. Ed’s Blog
Typically, an economy loses steam and enters a recession after a phase of over-investment, tight labor conditions, and an extended period of tight central bank monetary policies. Over the last seven years, we have experienced quite the opposite. Corporations have been very slow to invest or hire new employees. For those employees hired, many of them are “under-employed” (i.e., working part-time), or in other words, these workers desire more employment hours. The slower-than-expected growth has created an output gap. Scott Grannis at Calafia Beach Pundit estimates this gap to approximate $2.8 trillion (see chart below). The CBO expects a smaller gap estimate of about $580 billion to narrow over the next few years. By Grannis’ calculations, there is a reservoir of 5 -10 million jobs that could be tapped if the economy was operating more efficiently.













Leave A Comment