With the release of today’s report on September Personal Incomes and Outlays we can now take a closer look at “Real” Disposable Personal Income Per Capita.
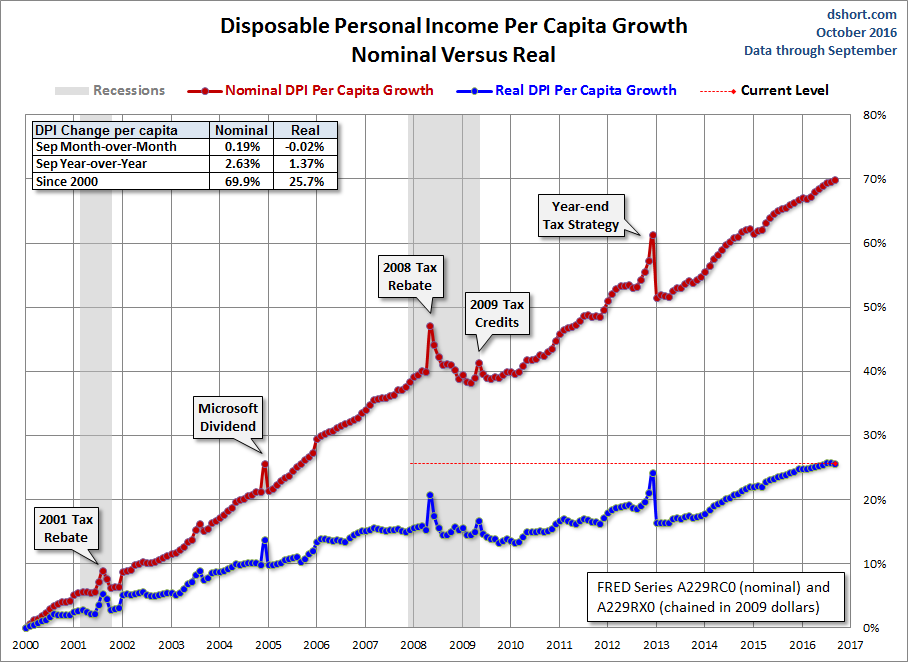
At two decimal places, the nominal 0.19% month-over-month increase in disposable income was essentially unchanged (-0.02%) when we adjust for inflation. The year-over-year metrics are 2.63% nominal and 1.37% real.
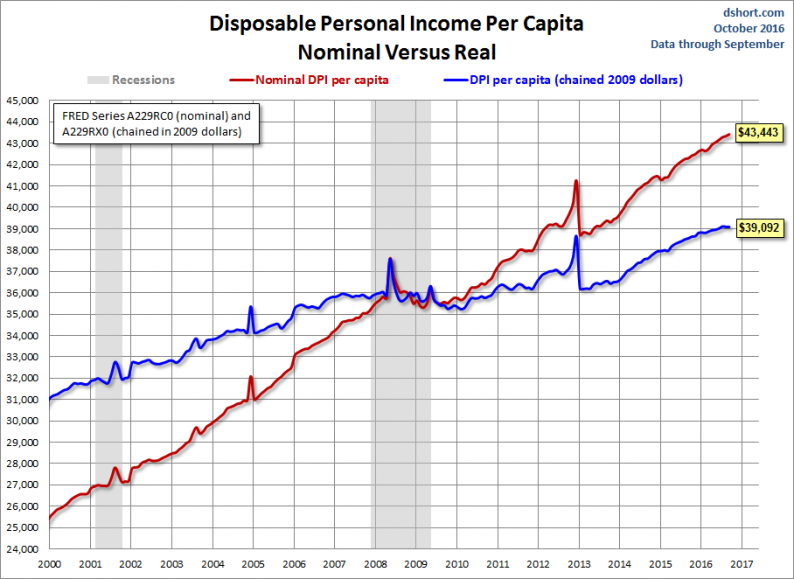
The first chart shows both the nominal per capita disposable income and the real (inflation-adjusted) equivalent since 2000. This indicator was significantly disrupted by the bizarre but predictable oscillation caused by 2012 year-end tax strategies in expectation of tax hikes in 2013.
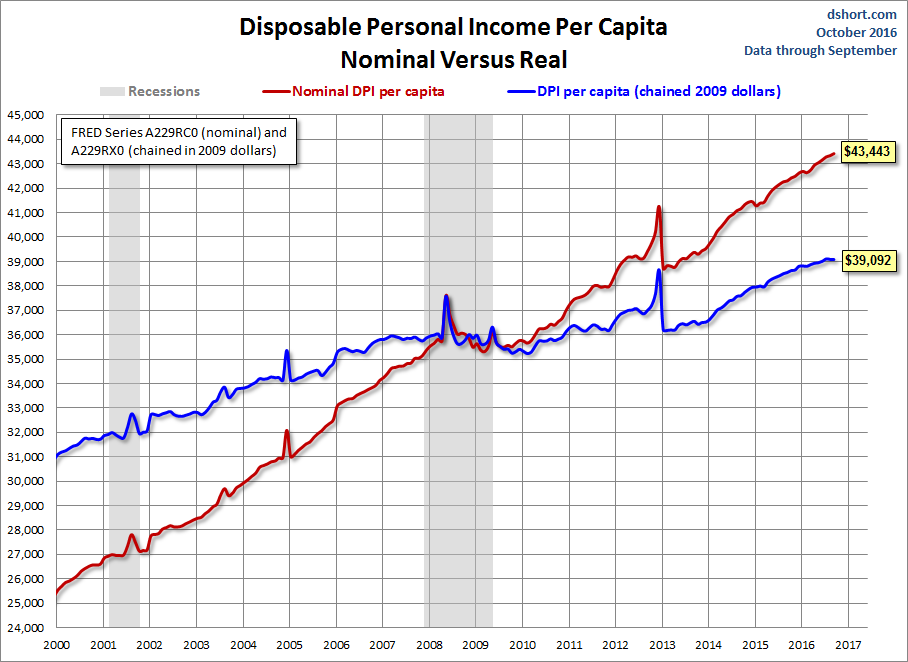
The BEA uses the average dollar value in 2009 for inflation adjustment. But the 2009 peg is arbitrary and unintuitive. For a more natural comparison, let’s compare the nominal and real growth in per capita disposable income since 2000. Do you recall what you were doing on New Year’s Eve at the turn of the millennium? Nominal disposable income is up 69.9% since then. But the real purchasing power of those dollars is up only 25.7%.
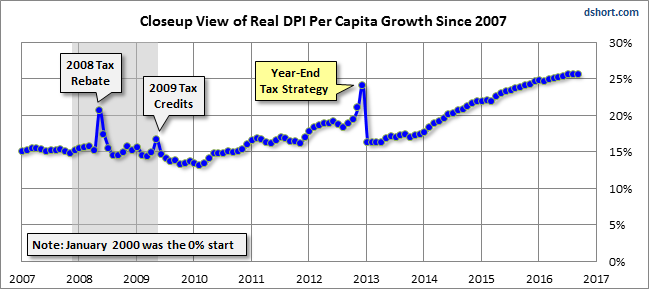
Here is a closer look at the real series since 2007.
DPI Per Capita
Let’s take one more look at real DPI per capita, this time focusing on the year-over-year percent change since the beginning of this monthly series in 1959. The chart below highlights the value for the months when recessions start to help us evaluate the recession risk for the current level.
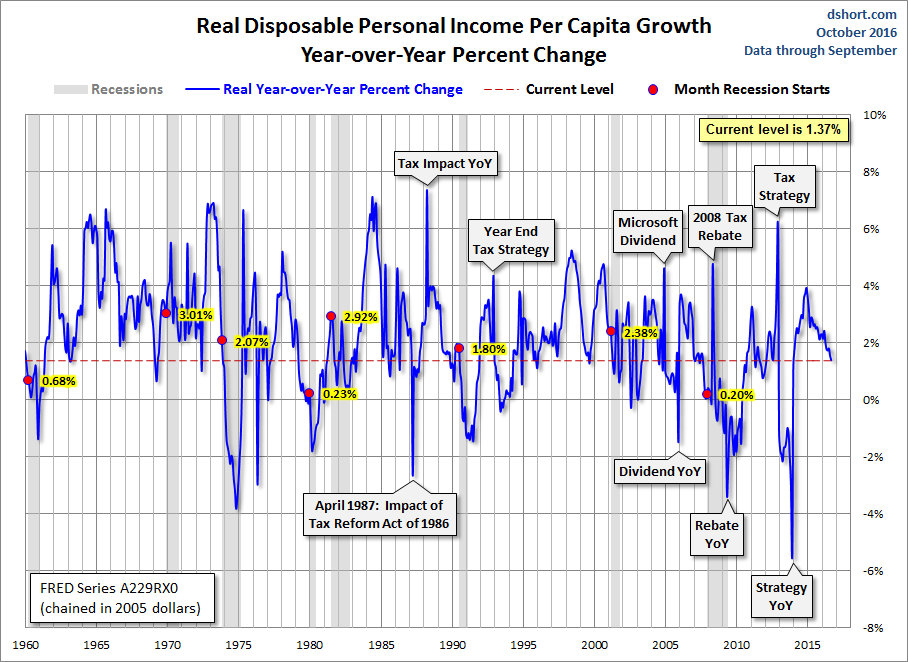
The current YoY of 1.37% is below the 1.66% average YoY at the start of the eight recessions since 1959. Check out the conspicuous tax planning blips as well as Microsoft’s big dividend payout in 2004.
Consumption versus Savings
The US is a consumer-driven economy, as is evident from the percent share of GDP held by Personal Consumption Expenditures.
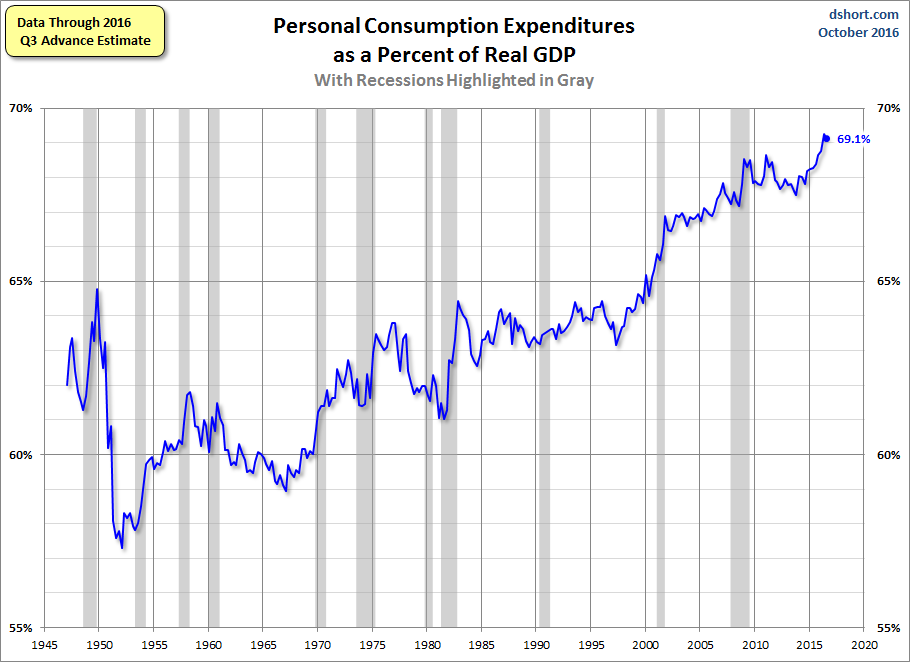
But the money to support consumption has to come from somewhere, and a growth in real disposable income would be the best source. An alternative is to spend more by reducing savings. Given the long timeframe, this chart features a log scale vertical axis to give a better view of the relative savings rate.










Leave A Comment