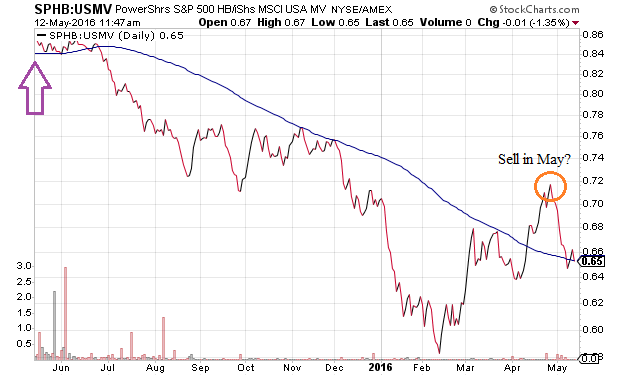
In a strong bull market, higher volatility stocks tend to outperform lower volatility stocks. The PowerShares S&P 500 High Beta (SPHB):iShares USA Minimum Volatility (USMV) price ratio demonstrates how the bull market in equities has been giving way since the highs in the Dow and the S&P 500 one year ago (May 2015).
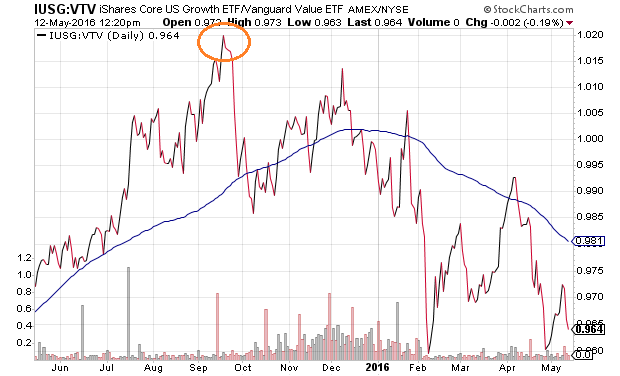
Similarly, in a strong bull market, growth-oriented assets tend to outperform value-oriented holdings. Instead, the iShares Core Growth (IUSG):Vanguard Value (VTV) price ratio illustrates a shift in preference from higher-flying growth securities to “safer” value stocks.
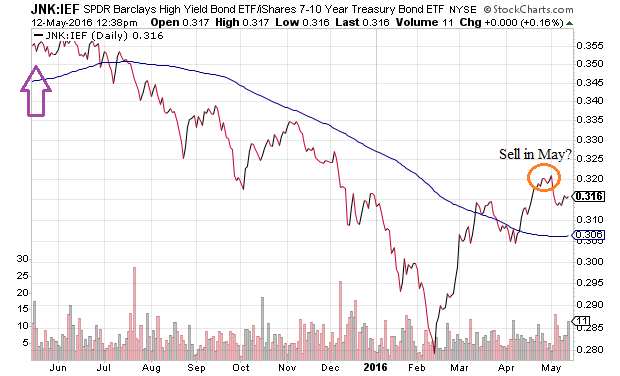
The hallmark of bullishness, indiscriminate risk taking, is no longer present in equities. It has been steadily eroding in bonds as well. Take a look at the SPDR High Yield Bond (JNK):iShares 7-10 Year Treasury (IEF) price ratio. The remarkable rally off of the February lows offered some “hopium” that the worst is over for junk debt. On the other hand, the long-term trend toward pursuing safety in treasuries as well as the likelihood of “sell in May” defensive posturing does not favor yield seeking speculation going forward.
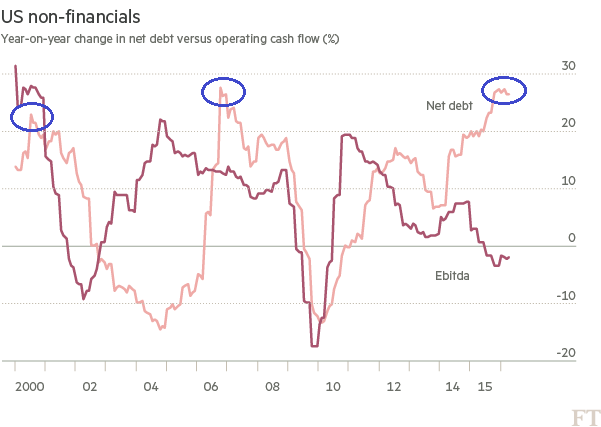
Perhaps risk taking will return in a meaningful manner soon. I doubt it. Valuation extremes would need to become valuation bargains or, at the very least, the Federal Reserve would need to expand its balance sheet (QE/QE-like activity) yet again. Low borrowing rates alone cannot do the trick when corporate earnings (EBITDA) are deteriorating, revenue is softening and the year-over-year percentage growth of net debt is exploding.
Consider the following chart from the Financial Times. Non-financial corporations found themselves leveraged to the hilt in 2000 and again in 2007. Bear market retreats of 50%-plus in stocks occurred shortly thereafter. Why should investors believe that this time is different?
The corporate debt balloon is going to be a problem even if central banks perpetually support asset prices through direct purchases and/or rate manipulating schemes. Ten years ago, companies carried $4.6 trillion in outstanding debt. Today? We’re looking at $8.2 trillion. The annualized growth rate of that debt far exceeds the growth rate of profitability or sales. Worse yet, HALF of the $8.2 trillion in corporate bonds is set to mature over the next five years. The implication? Any recession in the next five years will see the vast majority of corporations issuing new debt in an environment where their coupons will be at higher yields and their total total debts will be more difficult to service.














Leave A Comment