On November 2, 1983, President Ronald Reagan signed a law establishing a federal holiday for the birthday of Martin Luther King Jr., to be celebrated each year on the third Monday in January. As the legislation that passed Congress said: “such holiday should serve as a time for Americans to reflect on the principles of racial equality and nonviolent social change espoused by Martin Luther King, Jr..” Of course, the case for racial equality stands fundamentally upon principles of justice, not economics. But here are a few economics-related thoughts for the day from the archives:
1) Inequalities of race and gender impose large economic costs on society as a whole, because one consequence of discrimination is that it hinders people in developing and using their talents. In “Equal Opportunity and Economic Growth” (August 20, 2012), I wrote.
A half-century ago, white men dominated the high-skilled occupations in the U.S. economy, while women and minority groups were often barely seen. Unless one holds the antediluvian belief that, say, 95% of all the people who are well-suited to become doctors or lawyers are white men, this situation was an obvious misallocation of social talents. Thus, one might predict that as other groups had more equal opportunities to participate, it would provide a boost to economic growth. Pete Klenow reports the results of some calculations about these connections in “The Allocation of Talent and U.S. Economic Growth,” a Policy Brief for the Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research.
Here’s a table that illustrates some of the movement to greater equality of opportunity in the U.S. economy. White men are no longer 85% and more of the managers, doctors, and lawyers, as they were back in 1960. High skill occupation is defined in the table as “lawyers, doctors, engineers, scientists, architects, mathematicians and executives/managers.” The share of white men working in these fields is up by about one-fourth. But the share of white women working in these occupations has more than tripled; of black men, more than quadrupled; of black women, more than octupled.
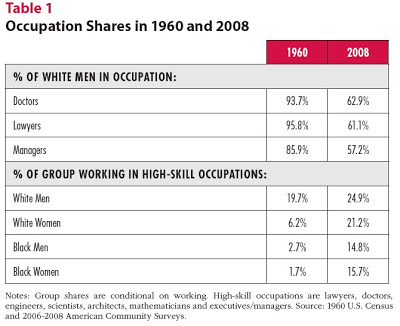
Moreover, wage gaps for those working in the same occupations have diminished as well. “Over the same time frame, wage gaps within occupations narrowed. Whereas working white women earned 58% less on average than white men in the same occupations in 1960, by 2008 they earned 26% less. Black men earned 38% less than white men in the typical occupation in 1960, but had closed the gap to 15% by 2008. For black women the gap fell from 88% in 1960 to 31% in 2008.”
Much can be said about the causes behind these changes, but here, I want to focus on the effect on economic growth. For the purposes of developing a back-of-the-envelope estimate, Klenow builds up a model with some of these assumptions: “Each person possesses general ability (common to
all occupations) and ability specific to each occupation (and independent across occupations). All groups (men, women, blacks, whites) have the same distribution of abilities. Each young person knows how much discrimination they would face in any occupation, and the resulting wage they would get in each occupation. When young, people choose an occupation and decide how
much to augment their natural ability by investing in human capital specific to their chosen
occupation.”
With this framework, Klenow can then estimate how much of U.S. growth over the last 50 years or so can be traced to greater equality of opportunity, which encouraged many in women and minority groups who had the underlying ability to view it as worthwhile to make a greater investment in human capital.
“How much of overall growth in income per worker between 1960 and 2008 in the U.S. can be explained by women and African Americans investing more in human capital and working more in high-skill occupations? Our answer is 15% to 20% … White men arguably lost around 5% of their earnings, as a result, because they moved into lower skilled occupations than they otherwise would have. But their losses were swamped by the income gains reaped by women and blacks.”
At least to me, it is remarkable to consider that 1/6 or 1/5 of total U.S. growth in income per worker may be due to greater economic opportunity. In short, reducing discriminatory barriers isn’t just about justice and fairness to individuals; it’s also about a stronger U.S. economy that makes better use of the underlying talents of all its members.
2) The black-white wage gap–and the share of the gap that is “unexplained”– is rising, not falling. Here’s part of what I wrote about in “Breaking Down the Black-White Wage Gap (September 6, 2017):
Mary C. Daly, Bart Hobijn, and Joseph H. Pedtke set the stage for a more insightful discussion in their short essay, “Disappointing Facts about the Black-White Wage Gap,” written as an “Economic Letter” for the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco (September 5, 2017, 2017-26). Here are a couple of figures showing the black-white wage gap, and then seeking to explain what share of that gap is associated with differences in state of residence, education, part-time work, industry/occupation, and age. The first figure shows the wage gap for black and white men; the second for black and white women.











Leave A Comment