When a currency peg breaks, it unleashes shock waves of uncertainty and repricing that hit the global financial system like a tsunami.
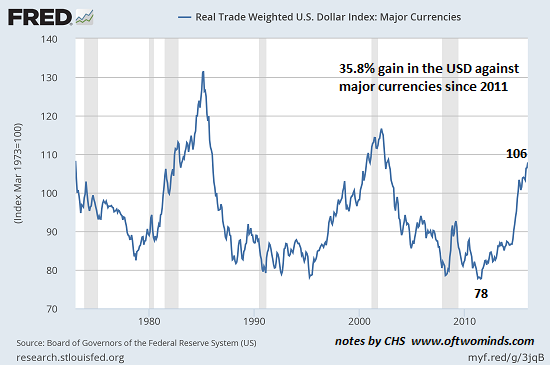
The U.S. dollar has risen by more than 35% against other major trading currencies since mid-2014:

If all currencies floated freely on the global foreign exchange (FX) market, this dramatic rise would have easily predictable consequences: everything other nations import that is priced in dollars (USD) costs 35% more, and everything the U.S. imports from other major trading nations costs 35% less.
For example, in the mid-1990s, the government/central bank of Thailand pegged the Thai currency (the baht) to the USD at the rate of 25 baht to the dollar.But some currencies don’t float freely on the global FX markets: they’re pegged to the U.S. dollar by their central governments. When a currency is pegged, its value is arbitrarily set by the issuing government/central bank.
Pegs can be adjusted up or down, depending on a variety of forces. But the main point is the market is only an indirect influence on the peg, not the direct price-discovery mechanism as it is with free-floating currencies.
If central states/banks feel their currency is becoming too strong via a vis the USD, they can adjust the peg accordingly.
Why do states peg their currency to the U.S. dollar? There are several potential reasons, but the primary one is to piggyback on the stability of the dollar without having to convince the market independently of one’s stability.
Another reason to peg one’s currency to the USD is to keep your currency weaker than the market might allow. This weakness helps make your exports to the U.S. cheap/ competitive with other nations that have weak currencies.
Nations defend their peg by selling dollars and buying their own currency. The way to understand this is supply and demand: if nobody wants the currency, the demand is low and the price falls. If there is strong demand for a currency, it rises in purchasing power if the supply is limited.











Leave A Comment