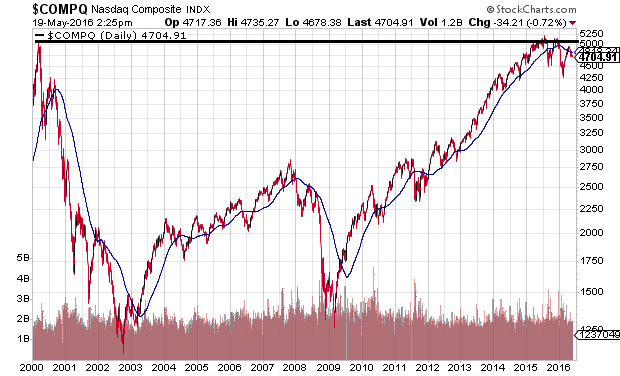
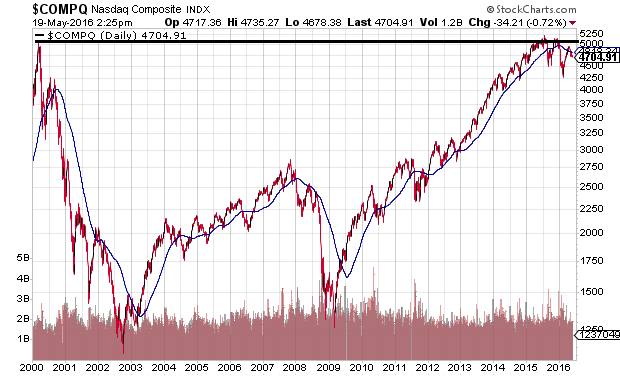
Some investors have come to believe that ultra-low interest rates alone have made traditional valuations obsolete. The irony of the error in judgment? Experts and analysts made similar claims prior to the Nasdaq collapse in 2000. The benchmark still trades below its nominal highs (and far below its inflation-adjusted highs) from 16 years ago.
Without question, exceptionally low borrowing costs helped drive current stock valuations to extraordinary heights. In fact, favorable borrowing terms played a beneficial role in each of the stock bull markets over the last 40-plus years, ever since the post-Volcker Federal Reserve began relying on the expansion of credit to grow the economy.
Indeed, we can even take the discussion one step further. Ultra-low interest rates had super-sized impacts on the last two bull markets in assets like stocks and real estate.
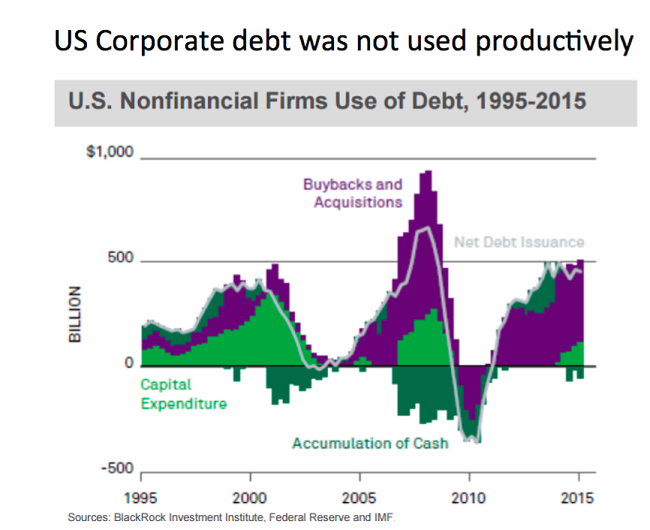
Bullishness from 2002-2007 occurred alongside household debt soaring beyond real disposable income; excessive borrowing at the household level set the stage for 40%-50% depreciation in stocks and real estate during the October 2007-March 2009 bear. Bullishness from 2009-2015 occurred alongside a doubling of corporate debt – obligations that moved away from capital expenditures toward non-productive buybacks and acquisitions. Would it be sensible to ignore the near-sighted nature of how corporations have been spending their borrowed dollars?
It is one thing to recognize that ultra-low borrowing costs helped to make riskier assets more attractive. It is quite another to determine that valuations have been rendered irrelevant altogether. For one thing, the U.S. had a low rate environment for nearly 20 years (i.e., 1935-1954) that is very similar to the current low rate borrowing environment. The price “P” that the investment community was willing to pay for earnings “E” or revenue (sales) still plummeted in four bearish retreats. In other words, low rates did not stop bear markets from occurring in 1937-1938 (-49.1%), 1938-1939 (-23.3%), 1939-1942 (-40.4%), or 1946-1947 (-23.2%).













Leave A Comment